Let’s build a strategic partnership to turn your AI vision into robust, scalable, and cost-effective solutions.
At Stepwise, we blend our deep-rooted expertise in Backend and Cloud technologies with cutting-edge AI to offer unparalleled AI Software Development services. Our services range from AI Backend Development and GPT Integration to AI Cloud Setup and MLOps & FinOps.



Paweł Wysocki
“At Stepwise, our expertise in Backend, Cloud, and AI technologies converge to transform your AI vision into scalable, cost-effective solutions.”
Diagram of Services
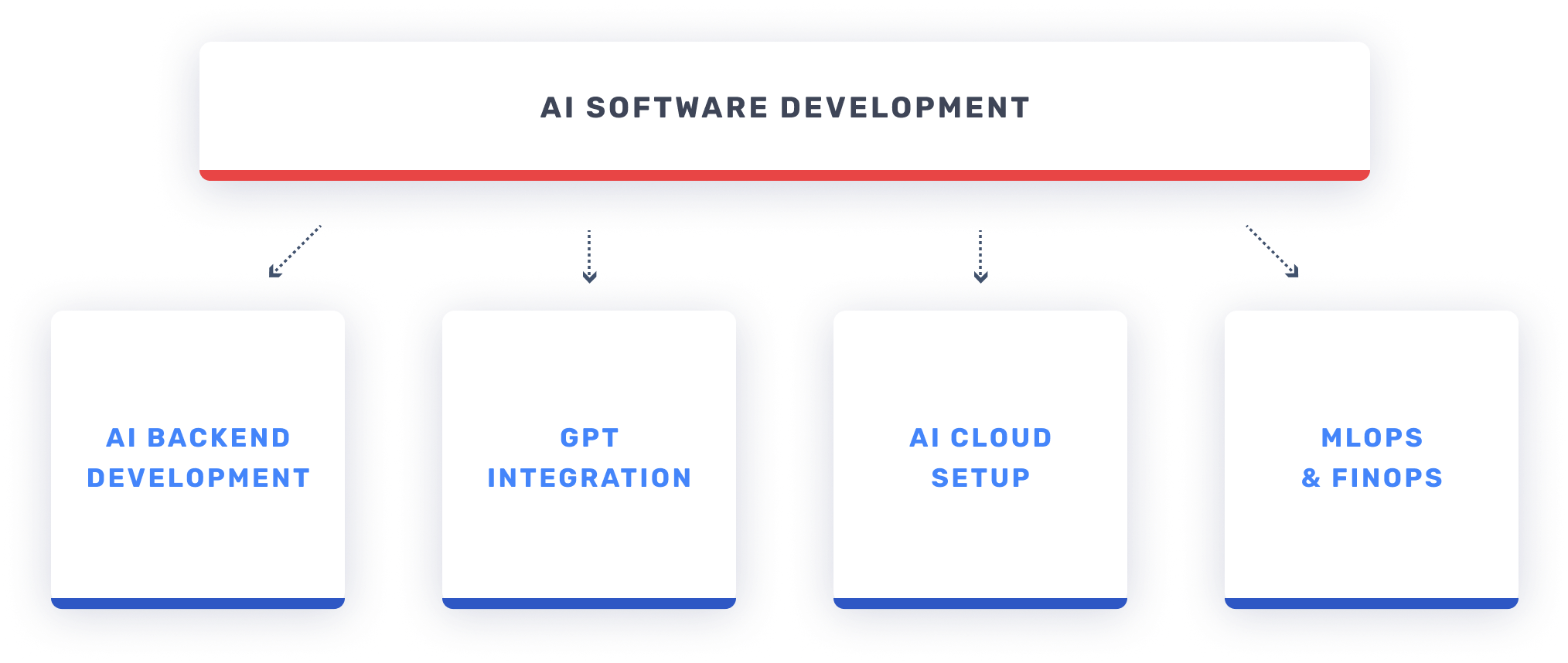
AI Backend Development
Unlock the full potential of your AI solutions with our expert AI Backend Development services.
Leveraging our roots in Java and mastery of Google Cloud Platform, we design robust AI software architecture, seamlessly integrate AI platforms, and ensure API interoperability. We are your one-stop solution for integrating generative AI into your existing systems.

AI Software Architecture
AI Platform Development
AI API Integration
Generative AI Integration
GPT Integration
Discover unprecedented business potential with Stepwise’s GPT Integration services.
Specializing in leveraging GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) and LLM (Language Learning Models) technologies, we streamline your text-based applications and elevate conversational interfaces to the next level. Seamlessly integrate GPT capabilities into your existing platforms, optimize for peak performance, and scale with confidence on Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
GPT Proof of Concept
GPT Models Optimisation
GPT Private Chat Setup
Custom GPT plugins
AI Cloud Setup
Stepwise’s AI Cloud Setup service is your go-to solution for all cloud-based AI needs. Leveraging our unmatched expertise in Google Cloud Platform (GCP), we provide seamless AI Cloud Infrastructure that integrates effortlessly with your existing systems.
Our offerings include cutting-edge Serverless Architectures for AI, robust Monitoring & Logging solutions, and proactive Resource Optimization for cost-effective operations. Experience unparalleled cloud performance and security as we accelerate your AI-powered digital transformation journey.

AI Cloud Infrastructure
Serverless Architectures for AI
Monitoring & Logging
Resource Optimisation

MLOps & FinOps
Stepwise’s MLOps & FinOps service streamlines your machine learning workflows and financial operations, anchoring them in reliability and efficiency.
We specialize in Continuous Model Training & Deployment, ensuring that your AI models are always up-to-date and high-performing. Our expertise extends to Model Governance & Auditability, Financial Monitoring & Optimization, and Cost-Performance Tuning, guaranteeing a scalable, compliant, and cost-effective AI operation.
Continuous Model Training & Deployment
Model Governance & Auditability
Financial Monitoring & Optimization
Cost-Performance Tuning
Fintech
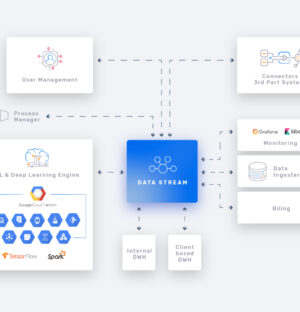
AI Platform for risk decision engineWe created a fully scalable SaaS platform, which is now successfully implemented by 4 end clients. We have conducted complex integrations with 3rd party solutions offering risk assessment and borrower verification services. We have made sure that the final product follows the PSD2 and GDPR guidelines.
Energy, Utilities, Smart Grid, Smart Cities
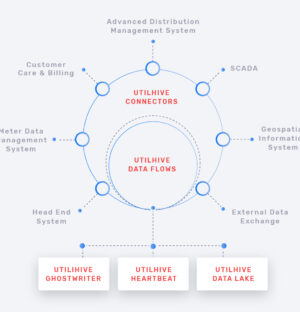
Smart Integration Platform for Digital UtilitiesThe platform itself is cloud native by definition and built around cutting-edge technologies. The main challenge was to help end customers integrate various systems easier and faster by providing pre-defined connectors, adapters and a monitoring system. Another challenge we had to face was management of complex data flows ...
Unstructured Data Analysis
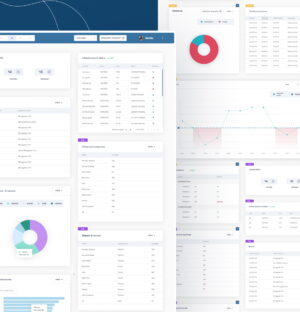
Interface for Smart Content FactoryA modern, efficient and scalable user interface was created for the Content Auto-tagging Manager system. On the basis of the refreshed application, the Customer may at any time be able to reuse components in the entire range of his applications.The outcome of our work is an improved end user journey experience, resulting ...
Explore all of our services groups
We provide a full-cycle AI & Machine Learning Development process – from Consulting, through Engineering to validate ML models, and ending with AI Software Development & Implementation.